Use a VIN Number to Check a Car's Options
A Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) is a 17-digit unique code given to a vehicle upon its production. It tells you the manufacturer, place of production, and the car's options. It is also useful information when talking to body shops and dealerships about the specifics of your vehicle. A VIN number is a great tool in checking the options on a car. With a little work, you’ll be able to locate the VIN, use it to get information on the manufacturer’s website, and get a vehicle history report from third party companies.
Contents
Steps
Locating the VIN
- Find the VIN on the car, if you have access to it. Most vehicles have the VIN etched or in the form of a sticker on at least two parts of the car. Look for the VIN on:
- The driver’s side in the door jamb
- The driver’s side dash board
- Metal within the engine compartment
- Parts of car that can’t be removed
- Look for the VIN on paperwork associated with the car. While you should be able to find the VIN on the actual car, it might be easier to find it on the car’s paperwork. This will come in handy if you don’t physically have the car, but have some paperwork associated with it. Look on the:
- Title
- Registration
- Repair records
- Ask the seller for the VIN. If you don’t own the car yet and can’t access it, you can ask the seller of the car for the VIN. The seller will be able to find the VIN just like you could – through paperwork or by looking on the body of the car.
- Make sure the seller provides you with the entire 17-digit VIN number before you commit to buying the vehicle.
- The seller should happily give you the number so that you can do an independent vehicle history search. If they don’t, they may be hiding something.
Using VIN Decoding Websites
- Find a website to give you details about the car. There are a variety of websites that offer VIN lookup services on the website. These websites will ask you to enter a car’s VIN, and then will supply you with information about the car’s options.
- Run an internet search for “free VIN lookup.”
- There are websites that provide free VIN lookup services. For example, try: https://www.northamericanmotoring.com/forums/vindecoder.php
- While some free VIN report services provide every detail of a car’s options, others do not.
- Some websites offer an advanced search for a fee.
- Enter your VIN. After you’ve found a website where you can look up your VIN, enter it in full. This is the most important step, and you need to follow the website’s directions. If you don’t, your search might work or it might return incorrect data.
- Follow the directions on the website and then press "search."
- Some websites may ask you to omit certain parts of the VIN number.
- Review the VIN detail report. After submitting the VIN number, you’ll get a report back. The report will detail the specifications of the car as it was produced by the manufacturer.
- The VIN report should include options, such as the transmission, the trim, and emissions specifications.
- The VIN report should include anything that was changed in the production process.
- VIN detail reports may not include options added after manufacturer, added at the dealership, or added by the consumer after the initial sale.
- Depending on the website, you may need to pay a fee for your VIN report.
Decoding the VIN
- Visit the manufacturer’s website. Once you’ve got the VIN number, you should log on to the internet and visit the manufacturer’s website. The carmaker’s website will contain resources that will help you decode the VIN and understand what each number means.
- Find the VIN decoder or search section of the website. Almost all manufacturers have a VIN decoder or similar tool on their website.
- Search through the tabs or search bar for "VIN decoder" or "VIN search."
- Click on the page or .pdf file that gives you information about decoding the VIN. For example, visit estore.honda.com/honda/parts/use-your-vehicle-vin.asp.
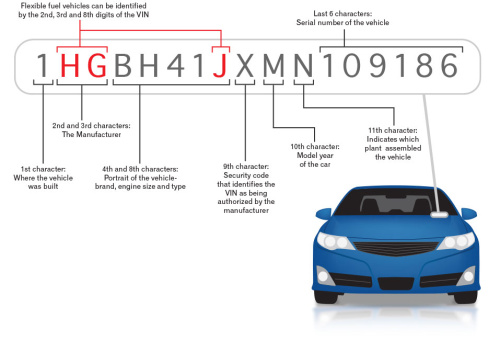
- Look at the world manufacturer identifier. The world manufacturer identifiers are the first 3 letters or numbers at the beginning of the VIN. This will give you information about the type of vehicle and where it was produced.
- The first number/letter tells the region the car was manufactured in, for example, “North America.”
- The second number tells the country.
- The third number tells the type of vehicle, for example “light truck.”
- Many different vehicles will share their first 3 numbers/letters.
- Identify the second sequence of numbers. The second sequence, numbers and letters 4 through 8, tell you more information about manufacturer options. By decoding these numbers, you’ll learn about the features the vehicle was manufactured with. These numbers will tell you info about the:
- Engine
- Model
- Body style.
- Skip the ninth digit. This is the digit used to verify that it is not a fraudulent VIN. It cannot be used to find information about the car.
- If you suspect the vehicle has a fake VIN number, contact the manufacturer.
- To decode this number, you may have to bring your car into a dealership.
- View the tenth digit. The tenth digit will tell you the model year of the vehicle. This is important to knowing the options on the vehicle, as different model years are equipped with different option group packages.
- This does not indicate what year the car was built. For example, if the car was a 2010 Chevrolet Equinox, it might have been constructed in late 2009
- This information should also be available in the vehicle’s manual or on other paperwork associated with the car.
- Find the last 7 digits. Along with the second sequence of numbers, these last digits are perhaps the most important for finding the options of the vehicle. They will give you all the car specific information you’re looking for.
- You’ll only be able to decode this information on the car manufacturer’s website.
- These numbers should give you information like that listed on the original sticker of the car.
- The numbers will also tell you what specific plant the vehicle was built as well as production specific information.
- Read about common options. While manufacturers use different codes to represent different options, the information encoded in the last 7 digits of your VIN number will provide specifics about a number of options. These numbers will give you info about common options like:
- Trim color
- Power seats and windows
- Entertainment system
- Seat covering material
- Sunroof
- Equipment packages like off road or towing
Purchasing a Vehicle History Report
- Submit your VIN to a third-party website. There are several companies that compile and sell vehicle history reports. A vehicle history report is a comprehensive history that includes data on a vehicle’s manufacture, sales, and sometimes repair information. Try websites like:
- Carfax
- Autocheck
- Pay a fee. After submitting your VIN, the third-party website may prompt you to pay a fee for a complete vehicle history report. While you may not want to pay, it is standard for companies to charge for this service.
- Feel free to shop around. Different websites or companies may offer different prices. In addition, some companies may run promos on vehicle history reports at different times.
- Fees normally range from between $20 to $40 dollars to receive a full vehicle history report.
- Some websites may provide cheaper rates per report if you want several vehicle history reports. For example, you may be able to get 5 reports for $59.99.
- Examine the report. Once you get your report back, you’ll need to take a good look at it so you can get a good idea of the car’s history, options, and other information. When reading the report:
- Verify the report matches the VIN you submitted.
- Read about the car's production and the vehicle's repair and registration history in the report.
- Look to see if the vehicle has been repaired or if the report shows any evidence of aftermarket upgrades.
Things You'll Need
- Vehicle Identification Number (VIN)
- Manufacturer's website
- $20 to $40 fee for a vehicle history report
Sources and Citations
- ↑ https://estore.honda.com/honda/parts/use-your-vehicle-vin.asp
- http://www.dmv.org/vehicle-history/find-vin.php
- http://www.flhsmv.gov/SafetyTips/PDFs/BuyingVehicle.pdf
- ↑ https://www.northamericanmotoring.com/forums/vindecoder.php
- ↑ http://researchmaniacs.com/VIN/VIN-Decoder.html
- http://vin.dataonesoftware.com/vin_basics_blog/bid/146754/why-you-shouldn-t-settle-for-a-vin-decoder-that-just-decodes-the-vin
- https://www.carfax.com/
- https://www.edmunds.com/how-to/how-to-quickly-decode-your-vin.html
- http://www.clark.com/free-vin-report